Increase particularly pronounced among mothers with lower education levels, Medicaid recipients, Black mothers
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
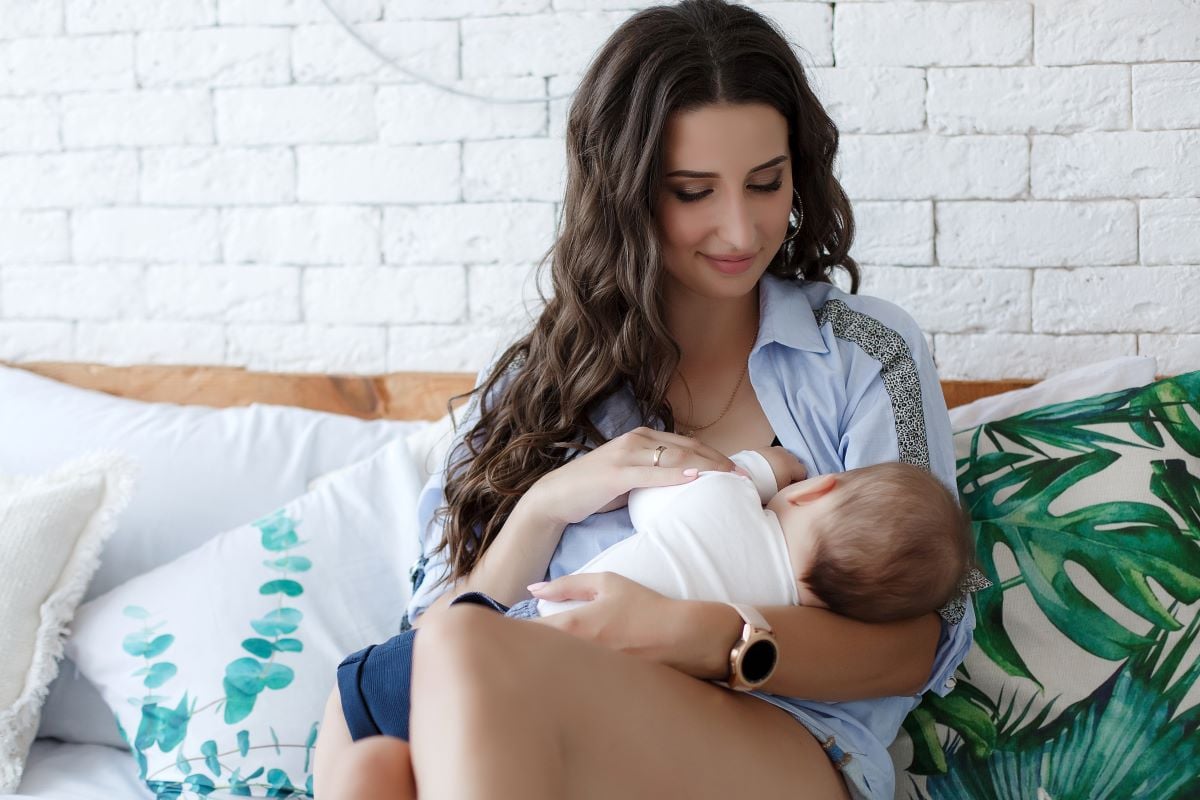
MONDAY, Dec. 30, 2024 (HealthDay News) — Average breastfeeding-initiation rates increased during the 2022 infant formula crisis and remained elevated at the end of the crisis, according to a study published online Dec. 30 in Pediatrics.
Luis Seoane Estruel, from the University of Connecticut in Storrs, and Tatiana Andreyeva, Ph.D., from the University of Connecticut in Hartford, examined the evolution of breastfeeding-initiation trends during the 2022 infant formula crisis. Average changes in breastfeeding-initiation trends were examined by analyzing 2016 to 2022 national birth certificate data from 47 states and the District of Columbia.
The researchers found that average breastfeeding-initiation rates increased by 1.96 percentage points during the 2022 infant formula crisis. Furthermore, at the end of the crisis, rates remained elevated above historical levels. Among mothers with lower education levels, those receiving Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children assistance, residents of less populated counties, Medicaid recipients, and Black mothers, the increase was particularly pronounced, possibly due to their greater reliance on formula feeding. The largest increase in breastfeeding initiation (6.06 percentage points) was seen for populations meeting all of these sociodemographic criteria. In 2022, preexisting disparities in breastfeeding initiation declined.
“The disproportionate changes for population groups with lower breastfeeding rates contributed to a reduction in preexisting disparities in breastfeeding initiation, suggesting an underlying potential for improvement,” the authors write.
Copyright © 2025 HealthDay. All rights reserved.