Findings seen in patients without conventional surgical or endovascular treatment options
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
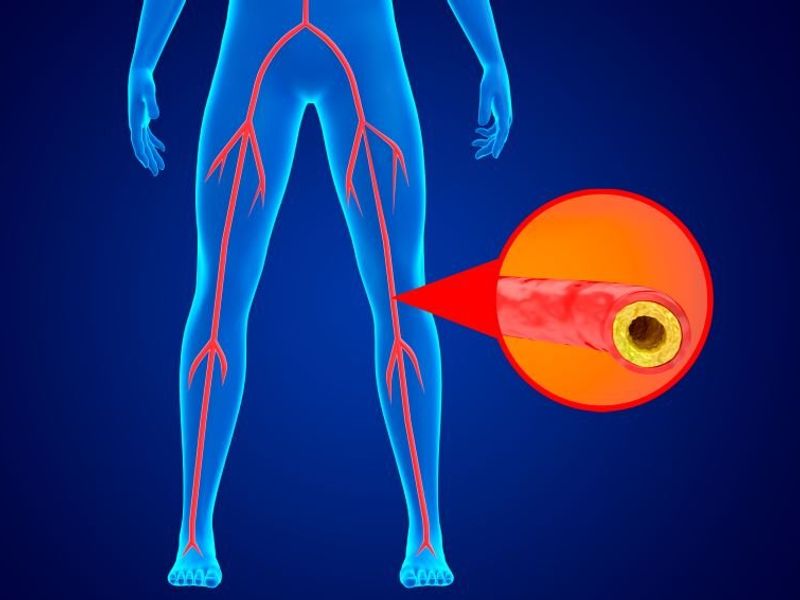
FRIDAY, March 31, 2023 (HealthDay News) — Transcatheter arterialization of the deep veins is safe for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia and no conventional surgical or endovascular revascularization treatment options, according to a study published online March 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Mehdi H. Shishehbor, D.O., from the University Hospitals Harrington Heart and Vascular Institute in Cleveland, and colleagues conducted a prospective multicenter study to examine the effect of transcatheter arterialization of the deep veins in patients with nonhealing ulcers and no surgical or endovascular revascularization treatment options. One hundred five patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia were enrolled; transcatheter arterialization of the deep veins was successfully performed in 104 patients.
The researchers found that 66.1 percent of the patients had amputation-free survival at six months. The posterior probability that amputation-free survival at six months exceeded a performance goal of 54 percent was 0.993 according to Bayesian analysis, which exceeded the prespecified threshold of 0.977. Sixty-seven patients (76.0 percent) attained limb salvage. Wounds were completely healed and in the process of healing in 25 and 51 percent of patients, respectively. There were no reports of unanticipated device-related adverse events.
“Transcatheter arterialization of the deep veins was safe and could be performed with a high degree of procedural success in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia and no conventional surgical or endovascular revascularization options to promote wound healing and prevent major amputation,” the authors write.
The study was funded by LimFlow.
Editorial (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.