Although faster adoption of robotic surgery has been seen in prostatectomy, with moderate diffusion in partial nephrectomy, and slow diffusion in total abdominal hysterectomy, the earliest delays in the adoption of robotic surgery might be explained by the high cost. 1
In partnership with PiperJaffray, Medgoo reached out to physicians to gather opinion on the current and future trends in robotic surgery. Forty-five physicians, across eight specialties including cardiology, neurology and oncology, responded to the survey questions and the following information was obtained:
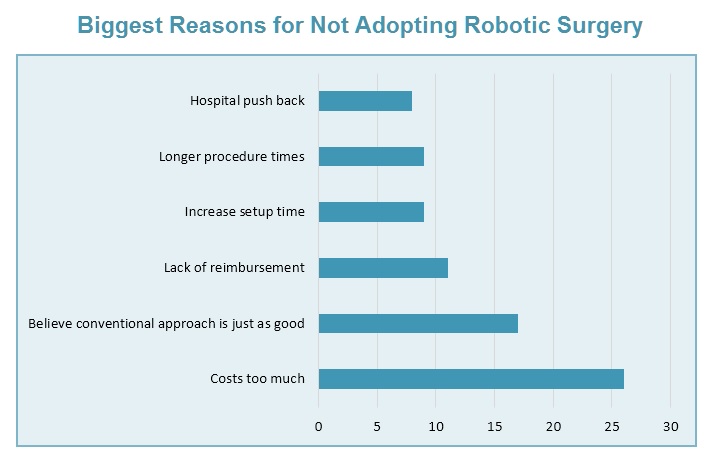
32.5% of physicians surveyed believe that cost is the biggest concern for why robotic surgery has not been adopted more widely.
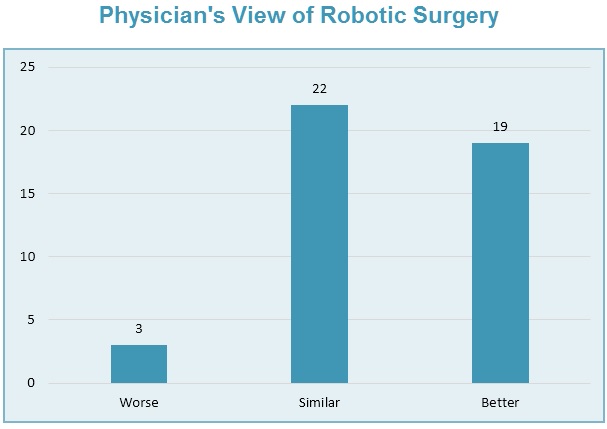
Over 90% of physicians surveyed believe that robotic surgery has similar or better outcomes than traditional surgery.
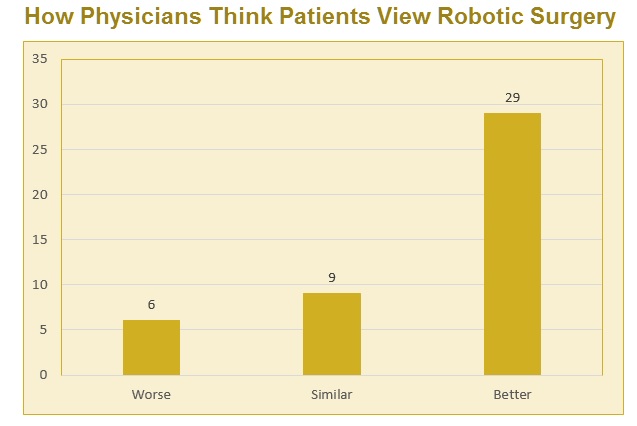
Over 86% of physicians surveyed think that patients believe robotic surgery has similar or better outcomes than the traditional approach.
25% of physicians surveyed believe that “access to hard-to-reach places” is the greatest benefit of robotic surgery.
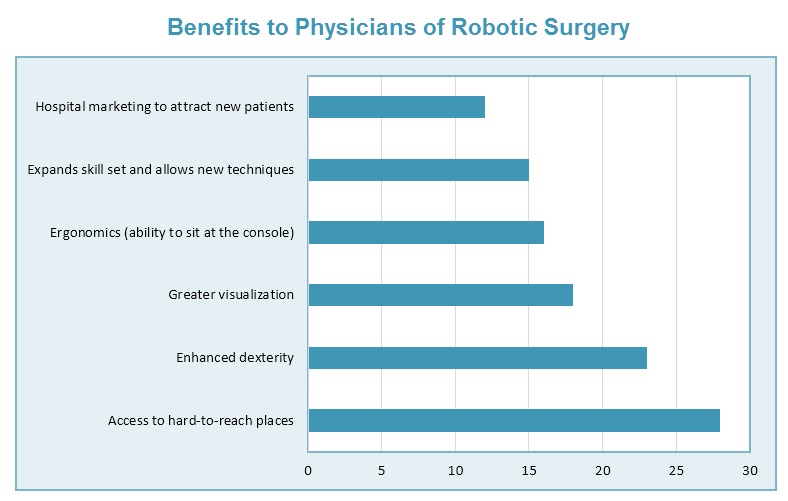
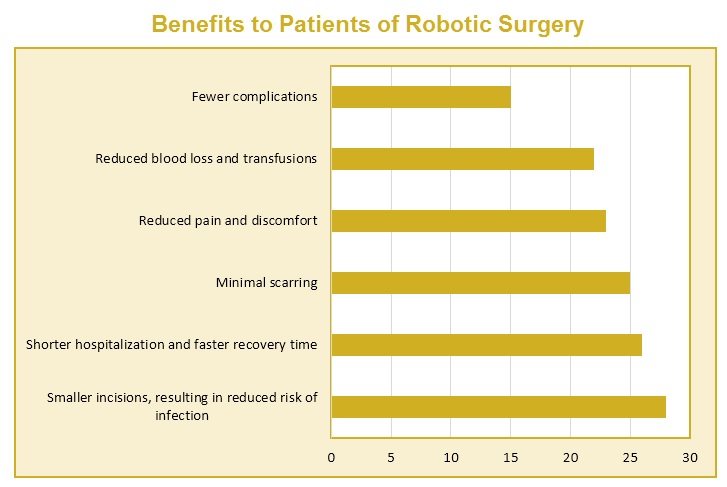
20% of physicians believe that smaller incisions, resulting in reduced risk of infection, is the greatest benefit to patients for robotic surgery. Another 18% believe that the greatest benefit is shorter hospitalization and faster recovery time.
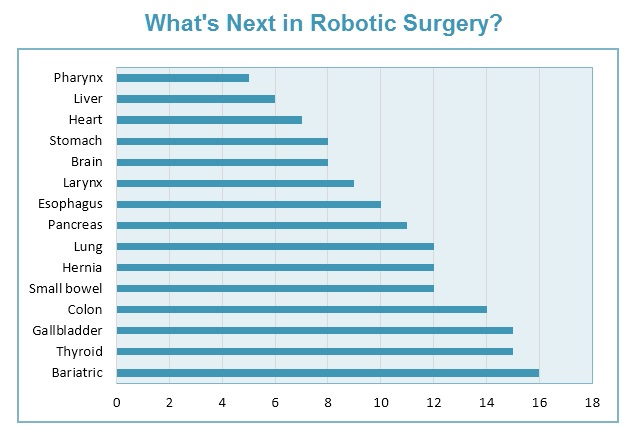
Physicians surveyed believe that bariatric surgery, followed by thyroid, gallbladder and colon have the most potential for growth in robotic surgery.
Works Cited:
1. Trends in the diffusion of robotic surgery: A retrospective observational study, PMC US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health, December 2017.